|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
News Archive
 This week we are highlighting the three finest examples of proteomics data made public in 2012. As we
have been doing for several years, we are naming the best data in three categories. N.B., these ratings
do not take into account the associated publication: only the data itself was considered in these
awards. Any of these data sets would be ideal for use as standards in the development of any type
of bioinformatics or computational biology algorithms associated with proteomics data.
This week we are highlighting the three finest examples of proteomics data made public in 2012. As we
have been doing for several years, we are naming the best data in three categories. N.B., these ratings
do not take into account the associated publication: only the data itself was considered in these
awards. Any of these data sets would be ideal for use as standards in the development of any type
of bioinformatics or computational biology algorithms associated with proteomics data.
Data set of the week: (2012/12/23)
Intermembrane space proteome of yeast mitochondria. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 30 MS/MS
data sets prepared using multidimensional chromatography and stable isotope labelling for relative
quantitation.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Voegtle FN, Burkhart JM, Rao S, Gerbeth C, Hinrichs J, Martinou JC, Chacinska A, Sickmann A, Zahedi RP and Meisinger C. in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 11:1840-52 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 30 MS/MS
data sets prepared using multidimensional chromatography and stable isotope labelling for relative
quantitation.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Voegtle FN, Burkhart JM, Rao S, Gerbeth C, Hinrichs J, Martinou JC, Chacinska A, Sickmann A, Zahedi RP and Meisinger C. in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 11:1840-52 (PubMed).
This data provided an unusually detailed look at the proteins associated with
mitochrondrial metabolism in baker's yeast (see this GO protein enrichment diagram
for an example of the level of enrichment obtained). The combination of good sample preparation, protein chemistry, separations
and mass spectrometry allowed the investigators to accurately distinguish between background levels of protein
flux and that specifically generated by the human sequence BAX:p treatment used in the experiments.
Data set of the week: (2012/12/16)
Tandem metal oxide affinity chromatography identifies novel in vivo MAP kinase substrates in Arabidopsis thaliana. Overall rating: 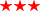 excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 6 MS/MS
data sets generated by a two step phosphoprotein/phosphopeptide affinity purification process.
The data files were made available through ProteomeXchange.
It was published by
Hoehenwarter W, Thomas M, Nukarinen E, Egelhofer V, Roehrig H, Weckwerth W, Conrath U and Beckers GJ in
Mol. Cell Proteomics November 20, 2012, mcp.M112.020560 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 6 MS/MS
data sets generated by a two step phosphoprotein/phosphopeptide affinity purification process.
The data files were made available through ProteomeXchange.
It was published by
Hoehenwarter W, Thomas M, Nukarinen E, Egelhofer V, Roehrig H, Weckwerth W, Conrath U and Beckers GJ in
Mol. Cell Proteomics November 20, 2012, mcp.M112.020560 (PubMed).
The data obtained in this study was an excellent example of combining protein and peptide
separations methods to obtain samples that were highly enriched in relatively rare materials. The results obtained
were very high quality, allowing the unambiguous identification of numerous biologically relevant phospho-domains
in MAPK signalling related proteins.
Data set of the week: (2012/12/9)
The quantitative proteomes of human-induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells. Overall rating:  excellent data (leading the field) excellent data (leading the field)
 This data set consisted of 220 MS/MS
data sets, including individual multidimensional chromatography and summary results.
The data files were made available through PeptideAtlas.
It was published by
Munoz J, Low TY, Kok YJ, Chin A, Frese CK, Ding V, Choo A, and Heck AJ in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:550 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 220 MS/MS
data sets, including individual multidimensional chromatography and summary results.
The data files were made available through PeptideAtlas.
It was published by
Munoz J, Low TY, Kok YJ, Chin A, Frese CK, Ding V, Choo A, and Heck AJ in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:550 (PubMed).
These experiments show what can be done using quantitative mass spectrometry methods
and several commonly available Orbitrap-based mass spectrometry technologies. The experiments were well executed
in a consistent manner and they should be quite reproducible. If you are interested in following the concentration
of any specific set of proteins in human embryonic stem cells, human-induced pluripotent stem cells or
the associated precursor fibroblast cell lines, it would be a good idea to consult this data set and use it
to select the appropriate technology for your experiments. While the quanitative method used in the study
(lysine/N-terminus derivatization with isotope-labelled dimethyl groups) may not be as popular as some
other protocols, all of the examples that we have seen have been well done, with a minimal number of side
reactions and artifacts.
Data set of the week: (2012/12/3)
Core proteome of the minimal cell: comparative proteomics of three mollicute species. Overall rating: 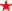 very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of one MS/MS
data set.
The data file were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Fisunov GY, Alexeev DG, Bazaleev NA, Ladygina VG, Galyamina MA, Kondratov IG, Zhukova NA, Serebryakova MV, Demina IA, and Govorun VM in
PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21964 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of one MS/MS
data set.
The data file were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Fisunov GY, Alexeev DG, Bazaleev NA, Ladygina VG, Galyamina MA, Kondratov IG, Zhukova NA, Serebryakova MV, Demina IA, and Govorun VM in
PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21964 (PubMed).
This data was interesting as it belongs to what has become a relatively rare class of
results: it contains the only identification information available for many proteins from a relatively common
bacterium: Acholeplasma laidlawii. A. laidlawii is a very small mycoplasma (a Mollicute genus with no
cell wall), which is can pass through sterilization filters with 0.2 µm pores. It also has a small genome (~1.5 Mbp),
with only 1380 genes. This single study found 819 translated proteins, a remarkable 59% of all possible translation
products, including > 100 proteins current labeled as "hypothetical".
 Yesterday (Thursday, November 29) we had a service interuption on many of our servers caused
by a change in the Internet Protocol addresses from our internet service provider. All of the
necessary changes have been made and should fully penetrate the global DNS system by the
end of business today. If you still have trouble accessing a particular server or service
tomorrow (December 1), please contact us and we will address the issue.
Yesterday (Thursday, November 29) we had a service interuption on many of our servers caused
by a change in the Internet Protocol addresses from our internet service provider. All of the
necessary changes have been made and should fully penetrate the global DNS system by the
end of business today. If you still have trouble accessing a particular server or service
tomorrow (December 1), please contact us and we will address the issue.
Data set of the week: (2012/11/26)
Combination of chemical genetics and phosphoproteomics for kinase signaling analysis enables confident identification of cellular downstream targets. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 96 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Oppermann FS, Grundner-Culemann K, Kumar C, Gruss OJ, Jallepalli PV and Daub H in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 11:O111.012351 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 96 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Oppermann FS, Grundner-Culemann K, Kumar C, Gruss OJ, Jallepalli PV and Daub H in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 11:O111.012351 (PubMed).
This data was an excellent example of how good phosphoproteomics measurements
have become using CID and an Orbitrap-LTQ. The level of phosphopeptide enrichment was very high (> 80%) and
multiply-phosphorylated peptides were very cleanly identified. The large neutral loss peaks that were so prominent
in the first generation of phosphopeptide CID spectra have been suppressed, making the identifications straightforward
without additional MS/MS/MS measurements. The sample preparation workflow used has generated phosphpeptides from
a significant number of proteins with poorly understood functions, such as NDEL1:p, TPD52L2:p, EML3:p and RAI1:p, that
have not been well sampled in previous large-scale phosphoproteomics experiments.
Data set of the week: (2012/11/18)
Identification of Proteins Associated with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Extracellular Matrix. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 4 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Toyofuku M, Roschitzki B, Riedel K, and Eberl L in
J Proteome Res 2012 11:4906-15 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 4 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Toyofuku M, Roschitzki B, Riedel K, and Eberl L in
J Proteome Res 2012 11:4906-15 (PubMed).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common bacteria that thrives
in many man-made environments. It is a human pathogen causing sepsis and generalized infections, particularly in
individuals with weakened immune systems. This well done study provides excellent insight into the proteins produced
by P.aeruginosa to form colony biofilm matrix material. The data is first rate and it is recommended for use as
a reference data set for examining the challenges associated with prokaryote proteomics for both protein and peptide sequence
assignment using spectra generated by CID in hybrid Orbitrap-LTQ instruments.
Data set of the week: (2012/11/11)
Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of neonatal and adult murine brain. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 3 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Goswami T, Li X, Smith AM, Luderowski EM, Vincent JJ, Rush J and Ballif BA in
Proteomics 2012 12:2185-9 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 3 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Goswami T, Li X, Smith AM, Luderowski EM, Vincent JJ, Rush J and Ballif BA in
Proteomics 2012 12:2185-9 (PubMed).
The data from this study showed a very good group phosphopeptide identifications
from murine brains, many of which were comparitively rare. The data also contained a significant subset of phosphopeptides
that were multiply phosphorylated, making it interesting from the view point of the mechanics of identifying this type of peptide.
The serine:threonine phosphorylation ratio for the identified peptides was ~5:1,
which is a common feature of mammalian S/T-phosphorylation studies.
 The Human Proteome Project has released its initial guidelines
for the submission of experimental data to the project. The stated purpose of these guidelines is as follows:
"At present, these guidelines lay out requirements for which types of files must be submitted where, and
by implication, the minimum amount of metadata describing the generation and handling of the data, since
a minimum amount of information is required to be accepted by the repositories. However, these guidelines
do not specify data quality metrics that must be met, as imposed by the MCP Guidelines, for example.
Such data quality metrics may become a future addition to these guidelines."
The Human Proteome Project has released its initial guidelines
for the submission of experimental data to the project. The stated purpose of these guidelines is as follows:
"At present, these guidelines lay out requirements for which types of files must be submitted where, and
by implication, the minimum amount of metadata describing the generation and handling of the data, since
a minimum amount of information is required to be accepted by the repositories. However, these guidelines
do not specify data quality metrics that must be met, as imposed by the MCP Guidelines, for example.
Such data quality metrics may become a future addition to these guidelines."
 A few months ago, we launched our first attempt at hosting a set of GPMDB web services based on a
REpresentational State Transfer (REST) API (see the API definition for details).
This new API has been a surprising success, with over 300,000 requests made in the first two months of
operation. Thanks to everyone who participated in the original Request for Comment process and the
developers who have created local applications that use the available services. Please let us know if you
have any suggestions for making things better, as we start the planning process for the 2.0 interface.
A few months ago, we launched our first attempt at hosting a set of GPMDB web services based on a
REpresentational State Transfer (REST) API (see the API definition for details).
This new API has been a surprising success, with over 300,000 requests made in the first two months of
operation. Thanks to everyone who participated in the original Request for Comment process and the
developers who have created local applications that use the available services. Please let us know if you
have any suggestions for making things better, as we start the planning process for the 2.0 interface.
Data set of the week: (2012/11/04)
Salivary basic proline-rich proteins are elevated in HIV-exposed seronegative men who have sex with men. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 2 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Burgener A, Mogk K, Westmacott G, Plummer F, Ball B, Broliden K, and Hasselrot K in
AIDS 2012 26:1857-67 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 2 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Burgener A, Mogk K, Westmacott G, Plummer F, Ball B, Broliden K, and Hasselrot K in
AIDS 2012 26:1857-67 (PubMed).
Unfortunately, only a limited number of the data files made available by the
researchers were retrievable from TRANCHE, but the two replicates that could be downloaded were very
good quality. The proteins and peptides found give an excellent guide to what can be sampled
using iTRAQ quantitation of clinical samples of human saliva. Saliva is a notoriously difficult
fluid to sample cleanly, but this study does an admirable job of obtaining good quality samples
and analyzing them thoroughly.
Data set of the week: (2012/10/28)
Global detection of protein kinase D-dependent phosphorylation events in nocodazole-treated human cells. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 18 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Franz-Wachtel M, Eisler SA, Krug K, Wahl S, Carpy A, Nordheim A, Pfizenmaier K, Hausser A and Macek B in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 11:160-70 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 18 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Franz-Wachtel M, Eisler SA, Krug K, Wahl S, Carpy A, Nordheim A, Pfizenmaier K, Hausser A and Macek B in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 11:160-70 (PubMed).
The data from this study were very good quality MS/MS spectra, representing what can be
expected from any collection of well done SILAC quantitation experiments. The results support the conclusions, however
our reanalysis of the data revealed a significant level of amide carbamylation. In addition to carbamylation, the
paper's analysis omitted deamidation, dioxidation and N-terminal cyclization, leading
to a false negative rate of >15% in the results reported in the paper. While these assignments do
not affect the biological conclusions in any major way, they do have an effect on the decoy-target calculation used to
estimate the peptide sequence assignment error rate. Any group interested in how false negative assignments alter the outcomes of
the statistical analysis of proteomics data should examine these results carefully.
Data set of the week: (2012/10/21)
TSLP signaling network revealed by SILAC-based phosphoproteomics. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 25 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Zhong J, Kim MS, Chaerkady R, Wu X, Huang TC, Getnet D, Mitchell CJ, Palapetta SM, Sharma J, O'Meally RN, Cole RN, Yoda A, Moritz A, Loriaux MM, Rush J, Weinstock DM, Tyner JW, and Pandey A in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 11:M112.017764 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 25 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Zhong J, Kim MS, Chaerkady R, Wu X, Huang TC, Getnet D, Mitchell CJ, Palapetta SM, Sharma J, O'Meally RN, Cole RN, Yoda A, Moritz A, Loriaux MM, Rush J, Weinstock DM, Tyner JW, and Pandey A in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 11:M112.017764 (PubMed).
This data was obtained from a well-planned study of the protein phosphorylation
dynamics of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin signalling system. The study used SILAC quantitative proteomics
and affinity purification to examine the changes in protein post-translational modification involved in this
particular system, which has been implicated in human disease. The SILAC method used (K6/R6) has become
increasingly popular recently, challenging the dominant K8/R10 method popularized by the Mann group.
Data set of the week: (2012/10/14)
The first comprehensive and quantitative analysis of human platelet protein composition allows the comparative analysis of structural and functional pathways. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 4 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Burkhart JM, Vaudel M, Gambaryan S, Radau S, Walter U, Martens L, Geiger J, Sickmann A, and Zahedi RP in
Blood 2012 120:e73-e82 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 4 MS/MS
data sets.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Burkhart JM, Vaudel M, Gambaryan S, Radau S, Walter U, Martens L, Geiger J, Sickmann A, and Zahedi RP in
Blood 2012 120:e73-e82 (PubMed).
This data set is a good example of the depth of proteomics analysis available
for simple cells. The proteome of platelets is simplified by the absence of nuclear proteins as well as
proteins involved in translation and folding. Therefore, they provide an insight into the minimum set
of proteins necessary to sustain cell metabolism and to perform the primary function of the platelet: the
formation of blood clots. The data is high quality and the results really do provide an excellent resource
for understanding the thrombocyte proteome.
 The Request for Comments GPM-2011.12.14 that details a nomenclature for
protein post-translational modifications has been updated to include a JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) nomenclature that
parallels the original compact text version. The addition of the JSON specification was made in response to
several reviewers who felt that developing parsers for the original compact text strings could be
a barrier-to-use for many applications. The relative simplicity of JSON and the existence of many
general-purpose JSON parsers should make the incorporation of this standard into data exchange systems somewhat
easier to implement for most potential users.
The Request for Comments GPM-2011.12.14 that details a nomenclature for
protein post-translational modifications has been updated to include a JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) nomenclature that
parallels the original compact text version. The addition of the JSON specification was made in response to
several reviewers who felt that developing parsers for the original compact text strings could be
a barrier-to-use for many applications. The relative simplicity of JSON and the existence of many
general-purpose JSON parsers should make the incorporation of this standard into data exchange systems somewhat
easier to implement for most potential users.
Data set of the week: (2012/10/7)
Integral Quantification Accuracy Estimation for Reporter Ion-based Quantitative Proteomics (iQuARI). Overall rating:  excellent data (leading the field) excellent data (leading the field)
 This data set consisted of 8 MS/MS
data sets generated from samples containing human and Pyrococcus furiosus proteins.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Vaudel M, Burkhart JM, Radau S, Zahedi RP, Martens L and Sickmann A in
J. Proteome Res, 2012 11:5072-5080 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 8 MS/MS
data sets generated from samples containing human and Pyrococcus furiosus proteins.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Vaudel M, Burkhart JM, Radau S, Zahedi RP, Martens L and Sickmann A in
J. Proteome Res, 2012 11:5072-5080 (PubMed).
This data demonstrates the use of a large set of standard peptides mixed in with
a sample for the purposes of quantitation. The standard peptides in this case were a whole cell digest
of the proteome of Pyrococcus furiosus, an Archaea hyperthermophile. This set of peptides provided
comparators present at a wide range of concentrations, with very little peptide sequence overlap with
the human sample being analyzed. Even though this data was generated mainly for the purposes of a bioinformatics
study, it was state-of-the-art in terms of chromatography and mass spectrometry. It was ideal for the purpose
of the paper and this set of spectra should be considered as a standard for use when testing algorithms involved
in proteomics data analysis and associated bioinformatics and computational biology studies.
Data set of the week: (2012/10/1)
Analysis of protein palmitoylation reveals a pervasive role in Plasmodium development and pathogenesis. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 10 MS/MS
data sets generated from samples enriched in palmitoylated proteins.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Jones ML, Collins MO, Goulding D, Choudhary JS and Rayner JC in
Cell Host Microbe, 2012 12:246-58 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 10 MS/MS
data sets generated from samples enriched in palmitoylated proteins.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Jones ML, Collins MO, Goulding D, Choudhary JS and Rayner JC in
Cell Host Microbe, 2012 12:246-58 (PubMed).
This ambitious study attempts to purify palmitoylated proteins from Plasmodium falciparum schizonts
obtained from Homo sapiens erythrocytes. The results show that they have generated fractions highly enriched in proteins with known
palmitoylation sites from both the malaria parasite and from human red blood cell membranes. The data is unusually high quality and
the methods used generated a rather complex problem in terms of peptide sequence assignments, protein identifications, computational biology and
bioinformatics.
 The GPM RFC 2012.09.01 that details how gene symbols will be used to reference DNA,
cDNA, RNA and protein sequences has been adopted.
The notation described in the RFC is meant to make discussions involving gene symbols and the macromolecule sequences associated
with that gene clearer, when necessary. The notation will be used in GPM/GPMDB report pages and associated spreadsheets.
This notation adds a suffix to existing gene names to specify the macromolecule, using the following convention:
":c" (cDNA); ":g" (genomic DNA); ":p" (protein) and ":r" (RNA).
The GPM RFC 2012.09.01 that details how gene symbols will be used to reference DNA,
cDNA, RNA and protein sequences has been adopted.
The notation described in the RFC is meant to make discussions involving gene symbols and the macromolecule sequences associated
with that gene clearer, when necessary. The notation will be used in GPM/GPMDB report pages and associated spreadsheets.
This notation adds a suffix to existing gene names to specify the macromolecule, using the following convention:
":c" (cDNA); ":g" (genomic DNA); ":p" (protein) and ":r" (RNA).
Data set of the week: (2012/09/23)
Extracellular polysaccharide-degrading proteome of Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 2 MS/MS
summaries constructed from SDS-PAGE gel bands.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Dunne JC, Li D, Kelly WJ, Leahy SC, Bond JJ, Attwood GT and Jordan TW in
J Proteome Res. 2012 11(1):131-42 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 2 MS/MS
summaries constructed from SDS-PAGE gel bands.
The data files were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Dunne JC, Li D, Kelly WJ, Leahy SC, Bond JJ, Attwood GT and Jordan TW in
J Proteome Res. 2012 11(1):131-42 (PubMed).
This well done study represents the first publicly available data that details the
polysaccharide-degradation proteome of one of the primary bacterial components of the ruminant digestion process,
Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus. Ruminant mammals (e.g., cattle) use an elaborate series of bacterial fermentation
reactions to digest plant-sourced polysaccharides into small molecules that can be used by normal mammalian
digestive metabolism. The proteins identified in this study provide the best list currently available of the
enzymes and transport molecules used by the microorganism to cope with the environment of the rumen.
 In a potentially interesting move, the European Proteomics Association has announced on
www.eupa.org that it has decided to
add a new open source journal as an alternative to its current journal of choice, the
Journal of Proteomics. This new publication,
EuPA Open Proteomics, will be an Elsevier title under Editor-in-Chief P. Verhaert. Part of the mandate
of the new journal will be to provide a forum for new types of manuscripts: "EuPA Open Proteomics will also accept
direct submissions from authors wishing to report on large data sets (submitted to raw data repositories) and
descriptive studies", which will be a welcome addition to the field.
In a potentially interesting move, the European Proteomics Association has announced on
www.eupa.org that it has decided to
add a new open source journal as an alternative to its current journal of choice, the
Journal of Proteomics. This new publication,
EuPA Open Proteomics, will be an Elsevier title under Editor-in-Chief P. Verhaert. Part of the mandate
of the new journal will be to provide a forum for new types of manuscripts: "EuPA Open Proteomics will also accept
direct submissions from authors wishing to report on large data sets (submitted to raw data repositories) and
descriptive studies", which will be a welcome addition to the field.
 The first version of a GPMDB API (Application Programming Interface) using REST (REpresentational State Transfer)
services is now complete, following a very successful Request for Comments
process. The full text of the service specifications is available here
This version of the interface is composed of twenty-three REST services, which return information in
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format. This format is commonly
used for exchanging information with mobile devices and has become a de facto standard for internet-based
APIs.
The first version of a GPMDB API (Application Programming Interface) using REST (REpresentational State Transfer)
services is now complete, following a very successful Request for Comments
process. The full text of the service specifications is available here
This version of the interface is composed of twenty-three REST services, which return information in
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format. This format is commonly
used for exchanging information with mobile devices and has become a de facto standard for internet-based
APIs.
Data set of the week: (2012/09/16)
Application of systems biology principles to protein biomarker discovery: urinary exosomal proteome in renal transplantation. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 7 MS/MS
analyses that were used for identification and pathway analysis.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Pisitkun T, Gandolfo MT, Das S, Knepper MA, and Bagnasco SM in
Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012 6:268-78 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 7 MS/MS
analyses that were used for identification and pathway analysis.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Pisitkun T, Gandolfo MT, Das S, Knepper MA, and Bagnasco SM in
Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012 6:268-78 (PubMed).
This set of measurements nicely characterizes the proteins present in
clinically isolated urinary exosomes (the membrane-bound particles shed by kidney nephrons). The proteins
detected show that the exosomes contain significant amounts of molecules originating from cellular plasma
membranes as well as those originating from blood plasma. The data was excellent, easy to interpret and
there was no indication of significant experimental bias or artifacts in the peptides identified.
 As part of our on-going relationship with the HUPO chromosome-based Human Proteome Project, we have
adopted an evidence code system for reporting whether a particular protein sequence has been
positively identified, indicating translation of the associated gene. This four level system has
been integrated into many of the GPMDB display pages by the addition of colored symbols indicating
the current status of the protein sequence associated with an accession number.
As part of our on-going relationship with the HUPO chromosome-based Human Proteome Project, we have
adopted an evidence code system for reporting whether a particular protein sequence has been
positively identified, indicating translation of the associated gene. This four level system has
been integrated into many of the GPMDB display pages by the addition of colored symbols indicating
the current status of the protein sequence associated with an accession number.
These evidence codes do not refer to the
quality of an individual protein identification in a data set: they are a property of
the all of information in GPMDB about a particular protein. The evidence code for any particular protein
accession number can be obtained using the GPMDB REST interface
and the meaning of the codes can be found a here.
These codes are assigned automatically by an algorithm that considers all of the evidence in GPMDB, so the
particular value of an evidence code is subject to change as the evidence for a given protein
changes and as the algorithm is improved.
Data set of the week: (2012/09/09)
Streptococcus pyogenes in Human Plasma ADAPTIVE MECHANISMS ANALYZED BY MASS SPECTROMETRY-BASED PROTEOMICS. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 41 MS/MS
analyses that were used both for protein identification and label-free quantitation.
The data files were made available through PeptideAtlas.
It was published by
Malmstrom J, Karlsson C, Nordenfelt P, Ossola R, Weisser H, Quandt A, Hansson K, Aebersold R, Malmström L, and Bjorck L in
J Biol Chem. 2012 287:1415-25 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 41 MS/MS
analyses that were used both for protein identification and label-free quantitation.
The data files were made available through PeptideAtlas.
It was published by
Malmstrom J, Karlsson C, Nordenfelt P, Ossola R, Weisser H, Quandt A, Hansson K, Aebersold R, Malmström L, and Bjorck L in
J Biol Chem. 2012 287:1415-25 (PubMed).
Streptococcus pyogenes is an important human pathogen, responsible for the diseases
generally classified as being caused by Group A Streptococcal (GAS) infection such as "strep throat", impetigo,
necrotizing fasciitis, scarlet fever and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. This study examined the proteome changes caused by the presence
of human plasma in the cells' environment, in an attempt to understand how the organism adapts when it moves from
its normal environment into human blood. The data quality is very good and
the identified sequences provide good examples of the peptides available for MS-based proteomics, in the HPLC
retention range of 20—40% acetonitrile.
 The Human Proteome Organization's 11th Annual Congress
opens tomorrow in Boston, Massachusetts. We would like to
congratulate the winners of this year's HUPO Awards: Carol Robinson (Award for a Distinguished Achievement in Proteomic Sciences);
Michel Desjardins (Award for Discovery in Proteomic Sciences); John Cottrell & David Creasy (Award for Science and Technology); and
Mark Baker (Award for Distinguished Service).
The Human Proteome Organization's 11th Annual Congress
opens tomorrow in Boston, Massachusetts. We would like to
congratulate the winners of this year's HUPO Awards: Carol Robinson (Award for a Distinguished Achievement in Proteomic Sciences);
Michel Desjardins (Award for Discovery in Proteomic Sciences); John Cottrell & David Creasy (Award for Science and Technology); and
Mark Baker (Award for Distinguished Service).
 This Request for Comment is based on a problem raised during
conversations on how use gene symbols in the Human Proteome Project when referring to proteins rather than the gene. Using gene
symbols for this purpose is common place in the literature, but it can be imprecise (and confusing) if the context is unclear
about the type of macromolecule being referenced. A wiki page for the RFC
GPM-2012.09.01 has been created. Suggestions are welcome and the period for comments ends on Sept. 14, 2012. This Request for Comment is based on a problem raised during
conversations on how use gene symbols in the Human Proteome Project when referring to proteins rather than the gene. Using gene
symbols for this purpose is common place in the literature, but it can be imprecise (and confusing) if the context is unclear
about the type of macromolecule being referenced. A wiki page for the RFC
GPM-2012.09.01 has been created. Suggestions are welcome and the period for comments ends on Sept. 14, 2012.
Data set of the week: (2012/09/02)
Functional Interplay between Caspase Cleavage and Phosphorylation Sculpts the Apoptotic Proteome. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 234 MS/MS
analyses, from multidimensional chromatography experiments that used both phosphopeptide enrichment and SILAC quantitation.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Dix MM, Simon GM, Wang C, Okerberg E, Patricelli MP, and Cravatt BF in
Cell 2012 150:426-40 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 234 MS/MS
analyses, from multidimensional chromatography experiments that used both phosphopeptide enrichment and SILAC quantitation.
The data files were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Dix MM, Simon GM, Wang C, Okerberg E, Patricelli MP, and Cravatt BF in
Cell 2012 150:426-40 (PubMed).
The data from this study has the potential to provide some interesting insights into
the use and reproducibility of proteomics techniques when applied to biological experiments. The work
does not highlight any specific technological innovation, but it does use existing techniques well and in a routine
manner. The sample preparation and handling appear to have been unusually good, with low levels of experimental artifact
modifications, making the data suitable for more indepth study for the detection of rarer post-translational modifications.
There are detectable levels of a few adventious proteins (bovine serum albumin, bovine casein and latex proteins), but no detectable
viral proteins. There is significant sensitivity drop-off for peptides that elute prior to 20% or later than 40% acetonitrile, but
this effect is consistent throughout the data.
Data set of the week: (2012/08/26)
The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster regulates multiple components of the TGF-β pathway in neuroblastoma. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of one set of selected MS/MS
analyses, obtained using combined fractional diagonal chromatography (COFRADIC) to enrich methionine-containing peptides and SILAC methods for
quantitation. This file were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Mestdagh P, Bostrom AK, Impens F, Fredlund E, Van Peer G, De Antonellis P, von Stedingk K, Ghesquiere B, Schulte S, Dews M, Thomas-Tikhonenko A, Schulte JH, Zollo M, Schramm A, Gevaert K, Axelson H, Speleman F and Vandesompele J in
Mol Cell. 2010 Dec 10;40(5):762-73 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of one set of selected MS/MS
analyses, obtained using combined fractional diagonal chromatography (COFRADIC) to enrich methionine-containing peptides and SILAC methods for
quantitation. This file were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Mestdagh P, Bostrom AK, Impens F, Fredlund E, Van Peer G, De Antonellis P, von Stedingk K, Ghesquiere B, Schulte S, Dews M, Thomas-Tikhonenko A, Schulte JH, Zollo M, Schramm A, Gevaert K, Axelson H, Speleman F and Vandesompele J in
Mol Cell. 2010 Dec 10;40(5):762-73 (PubMed).
This study provides an interesting insight into how COFRADIC can be used to reduce the complexity of
the peptides in protein identification experiments. The peptides found are significantly enriched in methionine, with almost 90% of
the identifications containing at least one Met residue. In combination with a simple SILAC method, protein quantitation was
obtained for a large number of peptides and identifications for more the 4,500 unique proteins. The use of proteomics
methods inconjunction with numerous biochemical methods to study microRNA
effects provided significant insight into pathway regulation in neuroblastoma cells.
Data set of the week: (2012/08/21)
Phosphoproteome dynamics upon changes in plant water status reveal early events associated with rapid growth adjustment in maize leaves. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 1598 LC/MS
analyses, including 798 MS/MS/MS runs. These files
were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Bonhomme L, Valot B, Tardieu F, and Zivy M in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2012 Jul 10 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 1598 LC/MS
analyses, including 798 MS/MS/MS runs. These files
were made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Bonhomme L, Valot B, Tardieu F, and Zivy M in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2012 Jul 10 (PubMed).
This interesting study contains a very large number of phosphopeptide identifications derived from
the leaves of the plant Zea mays (maize). The identifications are split between conventional CID MS/MS spectra and MS/MS/MS spectra
generated from the peaks corresponding to a neutral loss of -80 or -98 Da, caused by the loss of phosphate in the initial CID reaction. The study uses
chemical derivatization (light and heavy dimethylation) for quantitative analysis. These careful experiments provide some
interesting insights into the reaction of the plant to changes in water availability. They also are some of the best
proteomics observations made to date of this commercially important species.
Data set of the week: (2012/08/12)
Analysis of seminal plasma from patients with non-obstructive azoospermia and identification of candidate biomarkers of male infertility. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 12 LC/MS/MS
analyses from large composite MGF files constructed from the results of multidimensional chromatography experiments. These files
were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Batruch I, Smith CR, Mullen BJ, Grober E, Lo KC, Diamandis EP, and Jarvi KA in
J Proteome Res. 2012 11:1503-11 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 12 LC/MS/MS
analyses from large composite MGF files constructed from the results of multidimensional chromatography experiments. These files
were made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Batruch I, Smith CR, Mullen BJ, Grober E, Lo KC, Diamandis EP, and Jarvi KA in
J Proteome Res. 2012 11:1503-11 (PubMed).
The data contains some of the best identitifications currently available for many proteins specific to the
prostate and testis, such as
PATE1,
STEAP2, and
TGM4. It provides a very nice set of
examples of the proteins that can be reproducibly detected in seminal plasma using multidimensional
chromatography methods and they can be used to develop assays for specific proteins in this clinical sample. The
use of large, composite MGF files to report this type of data limits its utility for computational and
quantitative biology applications, because it is impossible to determine why the detected peptides are
biased against early eluting (< 20% ACN) sequences.
Data set of the week: (2012/08/05)
Plastid proteome assembly without Toc159: photosynthetic protein import and accumulation of N-acetylated plastid precursor proteins. Overall rating:  excellent data (leading the field) excellent data (leading the field)
 This data set consisted of 6 LC/MS/MS
analyses composed from one dimensional SDS-PAGE bands, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Bischof S, Baerenfaller K, Wildhaber T, Troesch R, Vidi PA, Roschitzki B, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Kessler F, Gruissem W, and Baginsky S in
Plant Cell. 2011 23:3911-28 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 6 LC/MS/MS
analyses composed from one dimensional SDS-PAGE bands, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Bischof S, Baerenfaller K, Wildhaber T, Troesch R, Vidi PA, Roschitzki B, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Kessler F, Gruissem W, and Baginsky S in
Plant Cell. 2011 23:3911-28 (PubMed).
This manuscript provides one of the largest, best sets of proteomics data from Arabidopsis thaliana cytosol
ever obtained using gel electrophoresis methods. The data is almost tailor made for bioinformatics investigations and
the development of peptide identification algorithms (much better than some of the truly low quality data proposed for this purpose).
For such a large experiment, the data quality is consistently high and the levels of experimental artifacts are
remarkably low.
Data set of the week: (2012/07/29)
The Evolutionary Imprint of Domestication on Genome Variation and Function of the Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus oryzae. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 8 LC/MS/MS
analyses, composed from multidimensional chromatography experiments made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Gibbons JG, Salichos L, Slot JC, Rinker DC, McGary KL, King JG, Klich MA, Tabb DL, McDonald WH, and Rokas A in
Curr Biol. 2012 Jul 10 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 8 LC/MS/MS
analyses, composed from multidimensional chromatography experiments made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Gibbons JG, Salichos L, Slot JC, Rinker DC, McGary KL, King JG, Klich MA, Tabb DL, McDonald WH, and Rokas A in
Curr Biol. 2012 Jul 10 (PubMed).
This data provides a remarkable insight into the changes caused by domestication in an industrial important fungus,
Aspergillus oryzae. It is used to malt rice and other starch sources, a necessary step in the creation of
a number of wines, spirits and sauces common in Asia. Its nearest wild relative,
Aspergillus flavus, is also economically significant, however
it is considered a source of spoilage in food and a common infectious agent in aspergillosis. The results presented here characterize the
differences in the enzymes exported from the fungus into the environment, which the organism uses to generate small molecules for
import back into its filaments. Simple inspection of the lists of proteins tell the story of how selection has been used to craft the
suite of digestive enzymes secreted by the fungus, from primarily cellulose and protein digestion (A. flavus) to starch and protein
(A. oryzae).
One feature of the data that was not mentioned in the article was the very high degree of non-tryptic proteolysis. Because the organisms both secrete
non-specific proteases, the resulting mixture of proteins was most
likely partially-digested prior to sampling and continued to have proteolytic activity during the trypsin digestion used for proteomics.
This multi-step proteolysis leads to an unusual set of peptides, with 40–70% of the peptides having at least one non-tryptic cleavage and an
unusual bias towards peptides with pI < 5.
Data set of the week: (2012/07/22)
Proteomics profiling of Madin-Darby canine kidney plasma membranes reveals Wnt-5a involvement during oncogenic H-Ras/TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 100 LC/MS/MS
analyses, composed of 96 one dimensional SDS-PAGE gel bands and four gel summaries, made available through PeptideAtlas
as entries PAe00375, PAe003695, PAe003691, & PAe003686.
It was published by
Chen YS, Mathias RA, Mathivanan S, Kapp EA, Moritz RL, Zhu HJ, and Simpson RJ in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2011, 10:M110.001131 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 100 LC/MS/MS
analyses, composed of 96 one dimensional SDS-PAGE gel bands and four gel summaries, made available through PeptideAtlas
as entries PAe00375, PAe003695, PAe003691, & PAe003686.
It was published by
Chen YS, Mathias RA, Mathivanan S, Kapp EA, Moritz RL, Zhu HJ, and Simpson RJ in
Mol Cell Proteomics, 2011, 10:M110.001131 (PubMed).
The data in this study is a good example of using one-dimensional SDS-PAGE to deal with membrane proteins.
The analysis of the data is straightforward and the group have done a good job of minimizing gel band contamination
with the common environmental proteins human KRT1, KRT2, KRT9, and KRT10, which can be an overwhelming presence in 1D gels. The
choice of Canis familiaris as the model species for the study gives an insight into the membrane proteins of a species that
has not be widely used for proteomics experiments, even though its complete genome has been known for many years. The lists of
proteins contain many prominent examples of proteins that are clearly present at significant levels in the organism
but which remain uncharacterized
(e.g., ENSCAFP00000021781,
ENSCAFP00000009106,
and ENSCAFP00000010256).
 The main GPMDB server came back online today at 21:00 UTC.
All of the tables affected were successfully restored from backup and the state of all GPMDB servers was
synchronized. We made a few changes so that hopefully this situation does not recur, but we will be
closely monitoring web usage for the next few days to be sure that the fixes are working. Ars longa, vita brevis. The main GPMDB server came back online today at 21:00 UTC.
All of the tables affected were successfully restored from backup and the state of all GPMDB servers was
synchronized. We made a few changes so that hopefully this situation does not recur, but we will be
closely monitoring web usage for the next few days to be sure that the fixes are working. Ars longa, vita brevis.
 GPMDB was taken off-line yesterday
because of an unexpected very high volume of requests that caused systems problems. The affected tables are being
rebuilt and we expect the server to come back on line today. If this is not possible, we will switch to
backup hardware this evening. This only affects requests directly to GPMDB: all of the search services
are still available and were not involved by this incident. GPMDB was taken off-line yesterday
because of an unexpected very high volume of requests that caused systems problems. The affected tables are being
rebuilt and we expect the server to come back on line today. If this is not possible, we will switch to
backup hardware this evening. This only affects requests directly to GPMDB: all of the search services
are still available and were not involved by this incident.
Data set of the week: (2012/07/08)
Proteomic analysis of extracellular matrix from the hepatic stellate cell line LX-2 identifies CYR61 and Wnt-5a as novel constituents of fibrotic liver. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 6 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Rashid ST, Humphries JD, Byron A, Dhar A, Askari JA, Selley JN, Knight D, Goldin RD, Thursz M, and Humphries MJ in
Proteomics. 2012 May 23. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100487 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 6 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Rashid ST, Humphries JD, Byron A, Dhar A, Askari JA, Selley JN, Knight D, Goldin RD, Thursz M, and Humphries MJ in
Proteomics. 2012 May 23. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100487 (PubMed).
This data provides a very nice insight into the extracellular matrix proteins being produced by
hepatic fibroblasts. These important proteins are most often mixed together with cellular proteins in clinical tissue samples
or discarded in cell culture experiments. These proteins are crucial to the formation and maintenance of tissues, but since they
cannot be effectively studied using the RNA-based techniques commonly used for intracellular proteins. The data supports the
conclusions in the associated manuscript, i.e., the differential presence of the relatively rare proteins WNT5A and CYR61.
 The July 2012 release of the GPMDB GHP
(click here) is a summary of
what we know about the expression of the 63,398 gene products (including alternate-splice variants) listed
by ENSEMBL, excluding all protein sequences for which the correspond RNA transcripts are marked as candidates for nonsense-mediated decay. The proteins reported in the GHP are organized
by the chromosomal location of the corresponding genes. In addition to the normal complement of autosomes and sex chromosomes, the
protein sequences originating on the mitochondrial chromosome and the chromosome 6 COX and QBL haplotypes are included.
This seventh edition of the GHP is available as a spreadsheet
or in web browser
format. The July 2012 release of the GPMDB GHP
(click here) is a summary of
what we know about the expression of the 63,398 gene products (including alternate-splice variants) listed
by ENSEMBL, excluding all protein sequences for which the correspond RNA transcripts are marked as candidates for nonsense-mediated decay. The proteins reported in the GHP are organized
by the chromosomal location of the corresponding genes. In addition to the normal complement of autosomes and sex chromosomes, the
protein sequences originating on the mitochondrial chromosome and the chromosome 6 COX and QBL haplotypes are included.
This seventh edition of the GHP is available as a spreadsheet
or in web browser
format.
 GPMDB has been collecting information about
amino acid polymorphisms (APs) for the last five years. The recorded information falls into two classes: APs
discovered using lists of specific, known SNPs loaded from dbSNP (that we refer to as SNAPs); and
APs discovered by checking all possible polymorphisms at each residue in a peptide. As of July 1, 2012 GPMDB has
information on approximately 4 million observation of APs from experimental data. This information has been
made available in two file formats. This information
will be updated quarterly. GPMDB has been collecting information about
amino acid polymorphisms (APs) for the last five years. The recorded information falls into two classes: APs
discovered using lists of specific, known SNPs loaded from dbSNP (that we refer to as SNAPs); and
APs discovered by checking all possible polymorphisms at each residue in a peptide. As of July 1, 2012 GPMDB has
information on approximately 4 million observation of APs from experimental data. This information has been
made available in two file formats. This information
will be updated quarterly.
 As of
June 30, 2012, there were only twenty-eight (28) peptide sequences that had been seen more than 1,000,000 times
in GPMDB. The characteristics that make a peptide eligible for the "More than a Million Club" are
not completely understood, but in general they are conserved as tryptic peptides in multiple species' orthologous genes as well as
alternate splices and paralogous genes, making them
eligible to be seen in many different types of experiments.
Here is the list of current members (click to see a list of the accession-number:#-of-observations pairs associated with each sequence): As of
June 30, 2012, there were only twenty-eight (28) peptide sequences that had been seen more than 1,000,000 times
in GPMDB. The characteristics that make a peptide eligible for the "More than a Million Club" are
not completely understood, but in general they are conserved as tryptic peptides in multiple species' orthologous genes as well as
alternate splices and paralogous genes, making them
eligible to be seen in many different types of experiments.
Here is the list of current members (click to see a list of the accession-number:#-of-observations pairs associated with each sequence):
Data set of the week: (2012/06/25)
Isolation and proteomic characterization of the mouse sperm acrosomal matrix. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 5 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Guyonnet B, Zabet-Moghaddam M, Sanfrancisco S, and Cornwall GA in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jun 15 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 5 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through TRANCHE.
It was published by
Guyonnet B, Zabet-Moghaddam M, Sanfrancisco S, and Cornwall GA in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jun 15 (PubMed).
This data distinguishes itself by sampling a rarely examined portion of the
proteome, the acrosomal matrix. This structure on sperm is responsible for attachment to
the egg in the first stage of the fertilization process. The associated proteins are not
commonly found in other tissues, so the samples examined here provide some of the best measurements
of these molecules — such as Akap3, Akap4, Odf2, Ropn1 and all of the acrosomal dynein subunits.
 With
its first 18 months of operations under its belt, ProteomeXchange
is set to deliver on seven items and two milestones at the end of June. These deliverables range from the first practical implementations of ProteomeXchange data
exports in LIMS systems to a new tutorial on the consortium. The following is a list of the deliverables ("D")
and milestones ("MS") expected on June 30: With
its first 18 months of operations under its belt, ProteomeXchange
is set to deliver on seven items and two milestones at the end of June. These deliverables range from the first practical implementations of ProteomeXchange data
exports in LIMS systems to a new tutorial on the consortium. The following is a list of the deliverables ("D")
and milestones ("MS") expected on June 30:
 The
HUPO 2012
meeting in Boston Massachusetts will be held on September 9-13, 2012. The deadlines for "Late-Breaking
Abstract Submission" and "Advance Registration" are both on June 30, 2012, so anyone interested
in attending this event should get their information in soon. This conference will be very important in
the definition and initial implementation of the chromosome- and biology/disease-based Human Proteome Projects,
so anyone interested in these large-scale proteome efforts should try to attend. The
HUPO 2012
meeting in Boston Massachusetts will be held on September 9-13, 2012. The deadlines for "Late-Breaking
Abstract Submission" and "Advance Registration" are both on June 30, 2012, so anyone interested
in attending this event should get their information in soon. This conference will be very important in
the definition and initial implementation of the chromosome- and biology/disease-based Human Proteome Projects,
so anyone interested in these large-scale proteome efforts should try to attend.
Data set of the week: (2012/06/17)
Proteomic analysis of the secretory response of Aspergillus niger to D-maltose and D-xylose. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
de Oliveira JM, van Passel MW, Schaap PJ, and de Graaff LH in
PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20865 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
de Oliveira JM, van Passel MW, Schaap PJ, and de Graaff LH in
PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20865 (PubMed).
These results comprise a large fraction of the publicly available data about
the Aspergillus niger proteome. While the organism is very common in the environment, it is not
one of the human pathogenic Aspergillus species, such as A. fumigatus or A. flavus.
A. niger is a very important industrial fungus, used mainly as a source of enzymes for food production.
This study does a nice job of creating an inventory of the secreted proteins normally expressed by the organism
under two common growth conditions, providing insights into the metabolic changes that are necessary
for growth when the environment changes. Secreted proteins are very important for fungi as
they are responsible for digesting nearby carbohydates and proteins into a form that the fungus can use
as food.
 We are announcing a new
RFC for the development a set of web services to
provide an interface for accessing information stored in GPMDB. After some research, we have
chosen to use the REST
architecture for these services, with JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)
as the format for information returned by these services. A draft
definition of a set of 14 services has been created and implemented. We would very much like to hear your comments
and suggestions for additional services as well as anything you might like to suggest regarding
the style, format or technology used. We are announcing a new
RFC for the development a set of web services to
provide an interface for accessing information stored in GPMDB. After some research, we have
chosen to use the REST
architecture for these services, with JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)
as the format for information returned by these services. A draft
definition of a set of 14 services has been created and implemented. We would very much like to hear your comments
and suggestions for additional services as well as anything you might like to suggest regarding
the style, format or technology used.
The following are a few examples of these services.
1. Find the number of times a peptide sequence has been seen: GET /1/peptide/count/seq=SPSSVEPVADMLMGLFFR 2. Find the number of times a protein sequence has been seen: GET /1/protein/count/acc=ENSMUSP00000026459 3. Find the phosphorylation sites for a protein & how often each was observed: GET /1/protein/modifications/acc=YKL112W&mod=80&res=STY&maxe=-2.0
The source code for the preliminary services and a demonstration client application
have been made available at the GPMDB FTP site.
This source code will be kept up-to-date with changes in the draft specification document.
Data set of the week: (2012/06/10)
Comprehensive proteomic analysis of influenza virus polymerase complex reveals a novel association with mitochondrial proteins and RNA polymerase accessory factors. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 22 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Bradel-Tretheway BG, Mattiacio JL, Krasnoselsky A, Stevenson C, Purdy D, Dewhurst S, Katze MG. in
J Virol. 2011 85:8569-81 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 22 LC/MS/MS
experiments, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Bradel-Tretheway BG, Mattiacio JL, Krasnoselsky A, Stevenson C, Purdy D, Dewhurst S, Katze MG. in
J Virol. 2011 85:8569-81 (PubMed).
The results nicely demonstrate previously unknown associations between
the influenza polymerase complex and host cell proteins. The experimental strategy was
well thought out and an appropriate number of replicates with and without infection were performed
to confirm that the findings of the study were valid. The experiments provide some of the
best observations to date of the influenza A virus RNA polymerase subunits PA, PB1 and PB2. These
observations should
be useful to anyone investigating the use of SRM/MRM techniques to detect these molecules in vivo.
Comparison of the peptides observed for the polymerase subunits of the strain used in this study
(H5N1 Vietnam/1203/04 isolate) provide an interesting case
study when they are compared with those observed for other strains of the
influenza virus.
Data set of the week: (2012/06/05)
Proteomic Analysis of S-Acylated Proteins in Human B Cells Reveals Palmitoylation of the Immune Regulators CD20 and CD23. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of one composition
of 2509 spectra obtained from multiple gel bands from an SDS-PAGE separation, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Ivaldi C, Martin BR, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Chapel A, Levade T, Garin J, and Journet A in
PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37187 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of one composition
of 2509 spectra obtained from multiple gel bands from an SDS-PAGE separation, made available through PRIDE.
It was published by
Ivaldi C, Martin BR, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Chapel A, Levade T, Garin J, and Journet A in
PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37187 (PubMed).
After spending the last few weeks dealing with the complexity of large collections
of mediocre data, it was a delight to find this gem. The authors have made excellent choices of the spectra
to include as evidence and they have retained enough common SDS-PAGE artifact proteins
so that the selected data retains the character of the original raw data. While some may be critical of this
process, it does provide good insight into the quality of the experiments and the type of data
used to support the conclusions in the paper. Note: CD20 and CD23 are annotated using their more
modern gene names, MS4A1 and FCER2, respectively. See the
HUGO Gene Nomenclature committee for CD molecules site for more information on the current status of
specific "CD" genes.
 As a research project,
GPM and GPMDB have focussed on trying to find innovative ways to use prior biological knowledge to
inform new measurements and add retrospective value to older ones. The systems that have been
built therefore focus on the retention of information and knowledge,
rather than the raw data used to generate that information/knowledge. Recent developments in the
field suggest that relying on external, government-funded resources to retain that
raw data may not be as reliable as we hoped. To address this problem, we have set up
an FTP archive (ftp.proteomecentral.org)
to try to maintain at least some of this data. Our first project, backing up the spectra in PRIDE, is
now complete and ready for use. The files are organized by their PRIDE data set ID number and can be
downloaded from the FTP site's PRIDE
folder at any time. As a research project,
GPM and GPMDB have focussed on trying to find innovative ways to use prior biological knowledge to
inform new measurements and add retrospective value to older ones. The systems that have been
built therefore focus on the retention of information and knowledge,
rather than the raw data used to generate that information/knowledge. Recent developments in the
field suggest that relying on external, government-funded resources to retain that
raw data may not be as reliable as we hoped. To address this problem, we have set up
an FTP archive (ftp.proteomecentral.org)
to try to maintain at least some of this data. Our first project, backing up the spectra in PRIDE, is
now complete and ready for use. The files are organized by their PRIDE data set ID number and can be
downloaded from the FTP site's PRIDE
folder at any time.
Data set of the week: (2012/05/27)
Identification of targets of c-Src tyrosine kinase by chemical complementation and phosphoproteomics. Overall rating:  excellent data (worth study) excellent data (worth study)
 This data set consisted of 7 result files from
phospho-tyrosine enrichment experiments using SILAC methods to obtain relative quantitation.
It was published by
Martinez-Ferrando I, Chaerkady R, Zhong J, Molina H, Kishore H, Herbst-Robinson K, Dancy BM, Katju V, Bose R, Zhang J, Pandey A, and Cole PA in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 11:M111.015750. (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 7 result files from
phospho-tyrosine enrichment experiments using SILAC methods to obtain relative quantitation.
It was published by
Martinez-Ferrando I, Chaerkady R, Zhong J, Molina H, Kishore H, Herbst-Robinson K, Dancy BM, Katju V, Bose R, Zhang J, Pandey A, and Cole PA in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 11:M111.015750. (PubMed).
This work nicely summarizes current trends in proteomics survey studies: early release
of data; high resolution parent
and fragment ion measurements; affinity methods to reduce sample complexity; and simple-to-interpret methods
for relative quantitation. This data set was released six months prior to publication, so any issues
relating to its quality or reproducibility could have been settled well before the conclusions were
published. The use of an Orbitrap in "high-high" mode made the identifications easy to
analyze and kept the false positive rate consistent and low (0.07-0.1%). The phospho-tyrosine peptide enrichment
method used worked well and resulted in high quality phospho-domain assignments. Finally, the appropriate
use of SILAC allowed the interpretation of the results to move beyond simply "yes" or "no" into a more nuanced
interpretation of the effects of changing c-Src tyrosine kinase activity.
Data set of the week: (2012/05/20)
Correct interpretation of comprehensive phosphorylation dynamics requires normalization by protein expression changes. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 15 result files from several
phospho-peptide enrichment/multidimensional chromatography experiments.
It was published by
Wu R, Dephoure N, Haas W, Huttlin EL, Zhai B, Sowa ME, and Gygi SP in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 10:M111.009654 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 15 result files from several
phospho-peptide enrichment/multidimensional chromatography experiments.
It was published by
Wu R, Dephoure N, Haas W, Huttlin EL, Zhai B, Sowa ME, and Gygi SP in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 10:M111.009654 (PubMed).
The data and experiments reported in this paper are part of a general
shift in attitude towards the detection of phosphorylated domains in proteins. Most of the work in
the previous decade has placed considerable emphasis on the technical aspects of identifying phosphopeptides
and the qualitative reporting of their observation. This work (and that of others) is now focused
on how to interpret the observation of phosphorylated protein domains in the context of a cell's
biological function. The experiments performed here were well done, resulting in a nice set of protein
and peptide identifications of the phosphoproteins involved in yeast metabolism.
Data set of the week: (2012/05/13)
Metabolic switches and adaptations deduced from the proteomes of Streptomyces coelicolor wild type and phoP mutant grown in batch culture. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 32 LC/MS/MS experiments
that were made available in mzData files via PRIDE.
It was published by
Thomas L, Hodgson DA, Wentzel A, Nieselt K, Ellingsen TE, Moore J, Morrissey ER, Legaie R; STREAM Consortium, Wohlleben W, Rodríguez-García A, Martín JF, Burroughs NJ, Wellington EM, and Smith MC in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Feb;11(2):M111.013797 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 32 LC/MS/MS experiments
that were made available in mzData files via PRIDE.
It was published by
Thomas L, Hodgson DA, Wentzel A, Nieselt K, Ellingsen TE, Moore J, Morrissey ER, Legaie R; STREAM Consortium, Wohlleben W, Rodríguez-García A, Martín JF, Burroughs NJ, Wellington EM, and Smith MC in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Feb;11(2):M111.013797 (PubMed).
These experiments give a good view into changes to the relative concentrations of many metabolic enzymes
in the environmental bacterium S. coelicolor in response to changes in phosphate-containing nutrient levels.
On the whole the experiments were well done, although there was significant, reproduced supression of
early eluting peptides in all of the LC/MS/MS runs. This supression may have made the experiments insensitive to
some particular enzymes. However, for enzymes containing observable peptides with gradient elutions > 20% acetonitrile,
the relative protein regulatory responses in could be inferred with reasonable accuracy from this data set.
 About a year ago (March 10, 2011), we added the capacity to associate any number of PSI-MS ontology terms with searches performed using the GPM public protein
identification system. This ontology contains more than 1,200 words and phrases specifically chosen by the
HUPO-PSI group. No one has used this feature of the
user interface. We will be discontinuing this interface feature as of May 14, 2012, because of this lack of use. Anyone
interested in maintaining this feature should send us an email (rbeavis@thegpm.org)
with their concerns. We will retain an archived version of the code use to generate this list at ftp.thegpm.org/repos/thegpm/tandem/psi-ms.js.
About a year ago (March 10, 2011), we added the capacity to associate any number of PSI-MS ontology terms with searches performed using the GPM public protein
identification system. This ontology contains more than 1,200 words and phrases specifically chosen by the
HUPO-PSI group. No one has used this feature of the
user interface. We will be discontinuing this interface feature as of May 14, 2012, because of this lack of use. Anyone
interested in maintaining this feature should send us an email (rbeavis@thegpm.org)
with their concerns. We will retain an archived version of the code use to generate this list at ftp.thegpm.org/repos/thegpm/tandem/psi-ms.js.
Data set of the week: (2012/05/07)
Cells lacking β-actin are genetically reprogrammed and maintain conditional migratory capacity. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS experiments
that were made available in mzData files via PRIDE.
It was published by
Tondeleir D, Lambrechts A, Mueller M, Jonckheere V, Doll T, Vandamme D, Bakkali K, Waterschoot D, Lemaistre M, Debeir O, Decaestecker C, Hinz B, Staes A, Timmerman E, Colaert N, Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J, and Ampe C in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Mar 22 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 2 LC/MS/MS experiments
that were made available in mzData files via PRIDE.
It was published by
Tondeleir D, Lambrechts A, Mueller M, Jonckheere V, Doll T, Vandamme D, Bakkali K, Waterschoot D, Lemaistre M, Debeir O, Decaestecker C, Hinz B, Staes A, Timmerman E, Colaert N, Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J, and Ampe C in
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Mar 22 (PubMed).
In this study, the authors use an unusual combination of SILAC relative quantitation and
combined fractional diagonal chromatography (COFRADIC) to study what happens to mouse embryonic fibroblast cells
when then lack an important cytoskeletal protein. Rather than the typical SILAC experiment in which heavy lysine and arginine
residues are used, this experimental design uses heavy methionine and COFRADIC to produce fractions enriched in peptides
containing oxidized methionine residues. While the use of an affinity technique has the potential to complicate
quantitative experiments, these experiments seem to have worked out quite well and generated some valuable
insights into the metabolic creativity shown by the fibroblasts in the face of what might seem to be an
insurmountable challenge.
 The good folks at ISB's PeptideAtlas have announced the
availability of what they are calling the Cow PeptideAtlas, derived from a set of experiments performed
by Emoke Bendixen, et al., at the Department of Animal Health and BioScience, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences,
Arhus University in Denmark. This collection of identifications can be accessed using the
ENSEMBL accession numbers for Bos taurus protein sequences, e.g. beta-lactoglobulin can be accessed
using ENSBTAP00000019538.
The data set currently available was mainly sourced from milk and colostrum. The entire data set, which also includes
udder tissue, mammary epithelium and hoof dermis, can be accessed in GPMDB, using the data set
keywords Bovine Peptideatlas or a
protein's accession number, ENSBTAP00000019538.
The good folks at ISB's PeptideAtlas have announced the
availability of what they are calling the Cow PeptideAtlas, derived from a set of experiments performed
by Emoke Bendixen, et al., at the Department of Animal Health and BioScience, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences,
Arhus University in Denmark. This collection of identifications can be accessed using the
ENSEMBL accession numbers for Bos taurus protein sequences, e.g. beta-lactoglobulin can be accessed
using ENSBTAP00000019538.
The data set currently available was mainly sourced from milk and colostrum. The entire data set, which also includes
udder tissue, mammary epithelium and hoof dermis, can be accessed in GPMDB, using the data set
keywords Bovine Peptideatlas or a
protein's accession number, ENSBTAP00000019538.
Data set of the week: (2012/04/29)
Kinome analysis of receptor-induced phosphorylation in human natural killer cells. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 3 LC/MS/MS experiments,
that were made available in the form of Mascot "DAT" files via TRANCHE.
It was published by
König S, Nimtz M, Scheiter M, Ljunggren HG, Bryceson YT, and Jänsch L. in
PLoS One. 2012 7:e29672 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 3 LC/MS/MS experiments,
that were made available in the form of Mascot "DAT" files via TRANCHE.
It was published by
König S, Nimtz M, Scheiter M, Ljunggren HG, Bryceson YT, and Jänsch L. in
PLoS One. 2012 7:e29672 (PubMed).
The results presented in this study make very good use of high accuracy mass measurements of both
parent and fragment ion for their biological application — determining phosphorylation changes in
natural killer (NK) cells caused by changes in receptor stimulation. These cytotoxic leucocytes are known to
have kinome changes associated with such stimulation, but the phosphorylation domain changes associated with
specific stimulations have not been fully explored. This paper makes a start in this type of interesting, cell-specific
investigation that makes use of clinically-derived cells for kinome study.
Data set of the week: (2012/04/22)
Quantification of mRNA and protein and integration with protein turnover in a bacterium. Overall rating:  very good data (specialist interest) very good data (specialist interest)
 This data set consisted of 42 LC/MS/MS runs from single dimension chromatography experiments.
It was published by
Maier T, Schmidt A, Güell M, Kühner S, Gavin AC, Aebersold R, and Serrano L. in
Mol Syst Biol 2011 7:511 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 42 LC/MS/MS runs from single dimension chromatography experiments.
It was published by
Maier T, Schmidt A, Güell M, Kühner S, Gavin AC, Aebersold R, and Serrano L. in
Mol Syst Biol 2011 7:511 (PubMed).
The data in these experiments give a good example of a straightforward analysis of the relationship between
protein and mRNA concentrations in a clinically important model organism, Mycoplasma pneumoniae. The results also
provide the best insights into the proteome of this prokaryote currently available, which has not be thoroughly studied even though
it has a comparatively simple genome and it is one of the primary causes of atypical bacterial pneumonia. The reproducibility
of this data was somewhat compromised by the consistent bias against early eluting peptides in the HPLC runs — very few peptides
that would be expected to elute at < 15% acetonitrile were observed.
Data set of the week: (2012/04/15)
Proteomic and phosphoproteomic comparison of human ES and iPS cells. Overall rating:  very good data (general interest) very good data (general interest)
 This data set consisted of 88 LC/MS/MS runs from multiple-dimensional chromatography experiments.
It was published by
Phanstiel DH, Brumbaugh J, Wenger CD, Tian S, Probasco MD, Bailey DJ, Swaney DL, Tervo MA, Bolin JM, Ruotti V, Stewart R, Thomson JA, and Coon JJ in
Nat Methods 2011 8:821-7 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 88 LC/MS/MS runs from multiple-dimensional chromatography experiments.
It was published by
Phanstiel DH, Brumbaugh J, Wenger CD, Tian S, Probasco MD, Bailey DJ, Swaney DL, Tervo MA, Bolin JM, Ruotti V, Stewart R, Thomson JA, and Coon JJ in
Nat Methods 2011 8:821-7 (PubMed).
The results here were a good representation of the proteins and phosphorylated domains that could be readily sampled
in human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. The techniques used were well described and
the measurements were in general very good. The studies were performed using a dual-cell quadrupole linear ion
trap-orbitrap hybrid mass spectrometer (dcQLT-Orbitrap), which produced high resolution, high accuracy parent and fragment ion measurements.
The data was made available through the authors' lab database site, the
Stem Cell-Omics Repository (SCOR).
 The set of bacterial and archae proteomes made available in the main GPM interface has been updated to include
527 new proteomes from a wide variety of new species and strains, bringing the total number of available proteomes to 1,607.
The new sequences have been added to all
of the public search servers — you may have to refresh your browser to get the new list if you have recently
used the search server web interface. This update brings the total number of prokaryote protein sequences
available for identification to 5.2 million. All of the existing species and strains have had their
sequences updated as well. The new sequences are available for download via FTP at
ftp.thegpm.org.
The set of bacterial and archae proteomes made available in the main GPM interface has been updated to include
527 new proteomes from a wide variety of new species and strains, bringing the total number of available proteomes to 1,607.
The new sequences have been added to all
of the public search servers — you may have to refresh your browser to get the new list if you have recently
used the search server web interface. This update brings the total number of prokaryote protein sequences
available for identification to 5.2 million. All of the existing species and strains have had their
sequences updated as well. The new sequences are available for download via FTP at
ftp.thegpm.org.
 A new edition of the Guide to the Human Proteome (GHP 2012.04.01)
has been released.
This collection is the only comprehensive listing of all of the protein sequences in the human proteome
currently identified by mass spectrometry, organized by
the chromosome of origin for each protein's transcript. The GHP is available in either spreadsheet or web browser (HTML) formats.
The new version has some signficant
improvements in the method of curation, most importantly close attention has been paid to the removal of transcripts that
correspond to mRNA non-stop and nonsense-mediated decay, which significantly reduces the complexity of alternate splicing for
many genes. The coverage of the GHP has been also been expanded by the 97.2 million new peptide identifications added to the underlying
GPMDB data sets in the three months since the last edition (GHP 2012.01.01).
A new edition of the Guide to the Human Proteome (GHP 2012.04.01)
has been released.
This collection is the only comprehensive listing of all of the protein sequences in the human proteome
currently identified by mass spectrometry, organized by
the chromosome of origin for each protein's transcript. The GHP is available in either spreadsheet or web browser (HTML) formats.
The new version has some signficant
improvements in the method of curation, most importantly close attention has been paid to the removal of transcripts that
correspond to mRNA non-stop and nonsense-mediated decay, which significantly reduces the complexity of alternate splicing for
many genes. The coverage of the GHP has been also been expanded by the 97.2 million new peptide identifications added to the underlying
GPMDB data sets in the three months since the last edition (GHP 2012.01.01).
 The main GPM system has been updated to use the latest version of the human proteome — ENSEMBL v. 66.37 — which was based on the
human genome sequence GRCh37.p6, Feb 2009. All of the
relevant resources (including annotated spectral library and proteotypic peptides) have been updated to the
new sequence set. The annotation file for human sNAPs (single Nucleotide Amino acid Polymorphisms) has been updated to dbSNP 135 (1,335,299 sNAPs). Approximately
1,400 new annotations have also been added to the protein sequence-specific modification specification file based on data that has
been collected by GPMDB and protein domain information.
The main GPM system has been updated to use the latest version of the human proteome — ENSEMBL v. 66.37 — which was based on the
human genome sequence GRCh37.p6, Feb 2009. All of the
relevant resources (including annotated spectral library and proteotypic peptides) have been updated to the
new sequence set. The annotation file for human sNAPs (single Nucleotide Amino acid Polymorphisms) has been updated to dbSNP 135 (1,335,299 sNAPs). Approximately
1,400 new annotations have also been added to the protein sequence-specific modification specification file based on data that has
been collected by GPMDB and protein domain information.
 In addition to naming an executive, the Human Proteome Project has announced the preliminary list
of country affliations for the groups that will carry out the chromosome-centric HPP. The list is not yet
complete, with eight chromosomes not yet assigned to particular groups. Some chromosomes, such as 12, have
been assigned to multinational groups that will collaborate to generate the necessary information. The mitochondrial
chromosome (MT), while listed below, is not yet an official part of the c-HPP.
In addition to naming an executive, the Human Proteome Project has announced the preliminary list
of country affliations for the groups that will carry out the chromosome-centric HPP. The list is not yet
complete, with eight chromosomes not yet assigned to particular groups. Some chromosomes, such as 12, have
been assigned to multinational groups that will collaborate to generate the necessary information. The mitochondrial
chromosome (MT), while listed below, is not yet an official part of the c-HPP.
 The Human Proteome Project has named its Executive Committee and Senior Scientific Advisory Board.
The members of these Committees will be tasked with co-ordinating the world-wide organization of the
member Projects as well as making the necessary scientific decisions about how and what the
member Projects will be providing to the overall project. These Committees will oversee both the chromosome-centric
and the biology and disease driven Projects and the three resource Pillars: a wide array of of mass spectrometry platforms,
the antibody-based Human Protein Atlas; and ProteomeXchange to integrate proteomics-based knowledge-bases.
The Human Proteome Project has named its Executive Committee and Senior Scientific Advisory Board.
The members of these Committees will be tasked with co-ordinating the world-wide organization of the
member Projects as well as making the necessary scientific decisions about how and what the
member Projects will be providing to the overall project. These Committees will oversee both the chromosome-centric
and the biology and disease driven Projects and the three resource Pillars: a wide array of of mass spectrometry platforms,
the antibody-based Human Protein Atlas; and ProteomeXchange to integrate proteomics-based knowledge-bases.
HPP Executive Committee
HPP Senior Scientific Advisory Board
Data set of the week: (2012/04/8)
Comparison of proteomic and transcriptomic profiles in the bronchial airway epithelium of current and never smokers. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 589 LC/MS/MS runs of 1D SDS-PAGE gel bands and experimental summaries.
The data was published by
Steiling K, Kadar AY, Bergerat A, Flanigon J, Sridhar S, Shah V, Ahmad QR, Brody JS, Lenburg ME, Steffen M, and Spira A in
PLoS One. 2009 4:e5043 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 589 LC/MS/MS runs of 1D SDS-PAGE gel bands and experimental summaries.
The data was published by
Steiling K, Kadar AY, Bergerat A, Flanigon J, Sridhar S, Shah V, Ahmad QR, Brody JS, Lenburg ME, Steffen M, and Spira A in
PLoS One. 2009 4:e5043 (PubMed).
This excellent study contrasted the proteomes of non- and current-smokers in
a very relevant tissue, bronchial airway epithelium. The results remain the definitive proteome
in this clinical tissue and contains some of the best observations for a number of rarely observed
proteins, such as TPPP3 (tubulin polymerization-promoting protein family member 3), SPATA18 (spermatogenesis associated 18 homolog),
ODF3B (outer dense fiber of sperm tails 3B), SPA17 (sperm autoantigenic protein 17) and ENSP00000387851 (member of the ciliary
rootlet coiled-coil family).
Data set of the week: (2012/04/1)
The matrisome: in silico definition and in vivo characterization by proteomics of normal and tumor extracellular matrices. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 98 LC/MS/MS runs and experimental summaries.
The data was published by
Naba A, Clauser KR, Hoersch S, Liu H, Carr SA, and Hynes RO in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2011 mcp.M111.014647 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 98 LC/MS/MS runs and experimental summaries.
The data was published by
Naba A, Clauser KR, Hoersch S, Liu H, Carr SA, and Hynes RO in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2011 mcp.M111.014647 (PubMed).
The idea behind collecting this data set was to define which proteins compose the
extracellular matrix and to discover which proteins would be contributed to the extracellular matrix by
the host in a xenograft experiment. The results do a good job of determining the protein complement of
this material in human tissue. The xenograft experiment — growing human-source tumours in live mice —
clearly shows that both the tumour cells and mouse host tissue contribute to the proteins in the tumour-associated
matrix. The value of the data was somewhat reduced by the relatively large number of detectable chemical artifacts,
particularly the carbamylation and carbamidomethylation of peptide N-terminii and lysine sidechains.
 Because of changes at Wormbase and
geneDB,
these resources are no longer suitable for our uses in proteomics. The use of both of these
sites and associated sequence resources will be discontinued as of May 1, 2012. They will be replaced with more
useful information sources. Because of changes at Wormbase and
geneDB,
these resources are no longer suitable for our uses in proteomics. The use of both of these
sites and associated sequence resources will be discontinued as of May 1, 2012. They will be replaced with more
useful information sources.
The RFA for a new FTP site for use by the chromosome-base Human Proteome Project has
been adopted. The new site designed to satisfy the RFA's requirements (ftp.proteomecentral.org)
is open and available for use. Any
c-HPP group interested in using the site for data storage should simply email Ron Beavis to
get their user name and password. The site is open to everyone for retrieving information — please read
the terms of use and
license for a better understanding
of how the site is meant to be used.
The protein sequences for the Brassica rapa (turnip) ENSEMBL proteome have been
added to the main search sites. This species is part of a large genus of plants that have been
broadly exploited as food, but the turnip is the first genome of the genus that has been fully
sequenced and interpretted.
Links to the Human Protein Reference Database (HPRD) have been removed from protein
evidence display pages because of licensing problems with that site. Links to the Human Metabolome Database
have also been removed from those pages, because an internal change at that site changed its behavior when
searching on gene names. If anyone have any suggestions for good replacements for these resources please
let us know.
Data set of the week: (2012/03/26)
Investigating the macropinocytic proteome of Dictyostelium amoebae by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of one large LC/MS/MS run.
The data was published by
Journet A, Klein G, Brugière S, Vandenbrouck Y, Chapel A, Kieffer S, Bruley C, Masselon C, and Aubry L in
Proteomics. 2012 12:241-5 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of one large LC/MS/MS run.
The data was published by
Journet A, Klein G, Brugière S, Vandenbrouck Y, Chapel A, Kieffer S, Bruley C, Masselon C, and Aubry L in
Proteomics. 2012 12:241-5 (PubMed).
Dictyostelium discoideum is one of the more peculiar organisms used in research. It is
a free-living "slime mold", commonly found in leaf litter on any temperate forest floor. In this study the
authors have characterized the proteins involved in the unusual method that the amoeboid form of this organism
uses to take in nutrients from the environment: macropinocytosis. The experimental methods used were very well done and the
results significantly extend what is known about both this process and the organism itself.
Data set of the week: (2012/03/18)
Proteogenomic analysis of Candida glabrata using high resolution mass spectrometry. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 70 LC/MS/MS
using both SDS PAGE protein and SCX peptide separation techniques.
The data was published by
Prasad TS, Harsha HC, Keerthikumar S, Sekhar NR, Selvan LD, Kumar P, Pinto SM, Muthusamy B, Subbannayya Y, Renuse S, Chaerkady R, Mathur PP, Ravikumar R, and Pandey A in
J Proteome Res. 2012 11:247-60 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 70 LC/MS/MS
using both SDS PAGE protein and SCX peptide separation techniques.
The data was published by
Prasad TS, Harsha HC, Keerthikumar S, Sekhar NR, Selvan LD, Kumar P, Pinto SM, Muthusamy B, Subbannayya Y, Renuse S, Chaerkady R, Mathur PP, Ravikumar R, and Pandey A in
J Proteome Res. 2012 11:247-60 (PubMed).
Candida glabrata is a haploid yeast (a.k.a., Torulopsis glabrata). It was long
thought to be a human commensal organism, but it has been shown to cause pathogenic infections
in immune-compromised individuals. This study of the organism's proteome, performed using FTMS with high resolution for
both the parent and fragment ions, provides a nice insight into the observable proteome of this poorly studied
species. It also provides an excellent set of data to compare with an existing (but relatively untested) genome sequence to
discover novel genes, understand the extent of amino acid polymorphisms and compare the post-translational modification
of domains with other, better studied, yeast species.
The Chromosome-Centric Human Proteome Project for cataloging proteins encoded in the genome (2012/03/17)
 Another proposal for a Human Proteome Project has been published as a Nature Biotechnology correspondence.
In this proposal, national groups will be organized to generate data and information about the proteins coded on individual chromosomes, with
countries being assigned one or more chromosomes. This article describes this effort at an executive level, mainly dealing with
the governance and organizational requirements of such a project. The SwissProt spin-off group, neXtprot,
has been chosen as the repository for the final results of this project, with ProteomeXchange serving as the conduit for preliminary data
dissemination. A web site hosted by the Institute for Systems Biology has been established for the overall HPP organization.
Another proposal for a Human Proteome Project has been published as a Nature Biotechnology correspondence.
In this proposal, national groups will be organized to generate data and information about the proteins coded on individual chromosomes, with
countries being assigned one or more chromosomes. This article describes this effort at an executive level, mainly dealing with
the governance and organizational requirements of such a project. The SwissProt spin-off group, neXtprot,
has been chosen as the repository for the final results of this project, with ProteomeXchange serving as the conduit for preliminary data
dissemination. A web site hosted by the Institute for Systems Biology has been established for the overall HPP organization.
 The first dataset that seems to be made available through ProteomeXchange has appeared in PRIDE (Pride ID 22134).
This data has been annotated with the ProteomeXchange accession number PXD000001 and has an associated Digital Object Identifier (DOI) 10.6019/PXD000001. The
URL associated with the DOI (http://central.proteomexchange.org/PXD000001) is
currently non-functional, but hopefully that will change soon. The associated data files are currently stored on an EBI FTP site, at
ftp://ftp.pride.ebi.ac.uk/2012/03/PXD000001. The normally
secretive ProteomeXchange group has not acknowledged this development, but hopefully they will make some official statement
about the proposed structure of the FTP site and the information to be made available through their "central.proteomexchange.org" web site
following their second annual meeting in San Diego.
The first dataset that seems to be made available through ProteomeXchange has appeared in PRIDE (Pride ID 22134).
This data has been annotated with the ProteomeXchange accession number PXD000001 and has an associated Digital Object Identifier (DOI) 10.6019/PXD000001. The
URL associated with the DOI (http://central.proteomexchange.org/PXD000001) is
currently non-functional, but hopefully that will change soon. The associated data files are currently stored on an EBI FTP site, at
ftp://ftp.pride.ebi.ac.uk/2012/03/PXD000001. The normally
secretive ProteomeXchange group has not acknowledged this development, but hopefully they will make some official statement
about the proposed structure of the FTP site and the information to be made available through their "central.proteomexchange.org" web site
following their second annual meeting in San Diego.
We will be mirroring relevant sections of the ftp.pride.ebi.ac.uk site through the GPMDB's FTP associated with
the c-HPP project in the folder "proteomexchange" (ftp.proteomecentral.org/proteomexchange). ProteomeXchange
accession numbers will be indexed in GPMDB and can be searched as a normal data set keyword. For example, this first entry can be accessed
using http://gpmdb.thegpm.org/PXD000001 or its
PRIDE ID using http://gpmdb.thegpm.org/data/keyword/PRIDE 22134.
Data set of the week: (2012/03/11)
The ethylmalonyl-CoA pathway is used in place of the glyoxylate cycle by Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 during growth on acetate. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 6 LC/MS/MS
runs from whole cell lysates of the organism grown under specific conditions.
The data was published by
Schneider K, Peyraud R, Kiefer P, Christen P, Delmotte N, Massou S, Portais JC, and Vorholt JA in
J Biol Chem. 2012 287:757-66 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 6 LC/MS/MS
runs from whole cell lysates of the organism grown under specific conditions.
The data was published by
Schneider K, Peyraud R, Kiefer P, Christen P, Delmotte N, Massou S, Portais JC, and Vorholt JA in
J Biol Chem. 2012 287:757-66 (PubMed).
This study effectively defined the observable proteome of Methylobacterium extorquens, a Gram-negative bacterium
that lives on plant leaves (click here
for an amusing short presentation on this organism). Even though the title of the study suggests that
the study may have limited scope, each LC/MS/MS run generated identifications for ~40% of the proteins coded in the
complete genome. The analysis presented in GPMDB used the proteomes from three stains of the organism — AM1, DM4 and PA1 —
to be sure that no genes were absent because of errors in the specific genome assembly of an individual
strain. This analysis showed that the AM1 strain assembly was very good, with only a small number of
proteins from the PA1 and DM4 proteomes found without corresponding AM1 orthologs.
Data set of the week: (2012/03/04)
Comparative proteomic analysis of eleven common cell lines reveals ubiquitous but varying expression of most proteins. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 181 LC/MS/MS
runs from lysates of 11 different laboratory cell lines.
The data was published by
Geiger T, Wehner A, Schaab C, Cox J, and Mann M in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 Jan 25 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 181 LC/MS/MS
runs from lysates of 11 different laboratory cell lines.
The data was published by
Geiger T, Wehner A, Schaab C, Cox J, and Mann M in
Mol Cell Proteomics 2012 Jan 25 (PubMed).
If you ever wanted to know what proteins were readily observable in
A549, GAMG, HEK293, HeLa, HepG2, K562,
MCF7, RKO, U2OS, Jurkat, HEK293, LnCap, HeLa or K562 cells, this is the data set for you. It is probably the
largest single data set generated for a publication using the current generation of Orbitrap technology. The
experiments were done using HCD fragmentation and consistent chromatographic and sample
preparation methods. The information is a good compliment to the earlier DSOTW Initial characterization of the human central proteome
where there is overlapping information generated with conventional CID.
Data set of the week: (2012/02/26)
Systematic phosphorylation analysis of human mitotic protein complexes. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 213 LC/MS/MS
affinity purification experiments.
The data was published by
Hegemann B, Hutchins JR, Hudecz O, Novatchkova M, Rameseder J, Sykora MM, Liu S, Mazanek M, Lénárt P, Hériché JK, Poser I, Kraut N, Hyman AA, Yaffe MB, Mechtler K, and Peters JM in
Sci Signal. 2011 4:rs12. (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 213 LC/MS/MS
affinity purification experiments.
The data was published by
Hegemann B, Hutchins JR, Hudecz O, Novatchkova M, Rameseder J, Sykora MM, Liu S, Mazanek M, Lénárt P, Hériché JK, Poser I, Kraut N, Hyman AA, Yaffe MB, Mechtler K, and Peters JM in
Sci Signal. 2011 4:rs12. (PubMed).
These results were good examples of the use of proteomics to target an aspect of a particular cell process, in
this case the role of phosphorylation in mitosis. The experimental protocols do a good job of isolating the
relavent proteins and generating easily interpretted phophopeptide spectra. The chromatography and
mass spectrometry were very well done and consistent across the data set. An unusual feature of this data set was
the presence of relatively strong signals from the protease domain (picornain 3C) of the human rhinovirus B-14 polyprotein. While
it is known that HeLa cells are susceptible to rhinovirus (common cold) infections, this data may be the first
experimental confirmation of a rhinovirus infection in cell culture based on proteomics methods.
 The US National Institutes of Health have issued a Request for Information entitled
"Disruptive
Proteomics Technologies - Challenges and Opportunities". This RFI is part of the
Common Fund initiative at the NIH. Hopefully the responses to this RFI will
better inform the working group of the real issues associated with proteomics in practice.
The first few paragraphs of the Purpose are given below:
The US National Institutes of Health have issued a Request for Information entitled
"Disruptive
Proteomics Technologies - Challenges and Opportunities". This RFI is part of the
Common Fund initiative at the NIH. Hopefully the responses to this RFI will
better inform the working group of the real issues associated with proteomics in practice.
The first few paragraphs of the Purpose are given below:
This RFI is directed toward determining how best to accelerate research in disruptive
proteomics technologies.
The Disruptive Proteomics Technologies (DPT) Working Group of the
NIH Common Fund wishes to
identify gaps and opportunities in current technologies and methodologies related to
proteome-wide measurements. For the purposes of this RFI, "disruptive" is defined as very
rapid, very significant gains, similar to the "disruptive" technology development that occurred
in DNA sequencing technology.
 The schedule for the European Proteomics Association's 2012 Basic Course program has
been announced. The courses are meant to
provide a theoretical basis to help students understand modern proteomics techniques;
illustrate how the techniques are being applied in modern proteomics studies
and provide practical instruction in laboratory techniques.
The schedule for the European Proteomics Association's 2012 Basic Course program has
been announced. The courses are meant to
provide a theoretical basis to help students understand modern proteomics techniques;
illustrate how the techniques are being applied in modern proteomics studies
and provide practical instruction in laboratory techniques.
The courses are as follows:
 This data set consisted of 59 LC/MS/MS
runs from U2-OS cell lysates.
The data was published by
Beck M, Schmidt A, Malmstroem J, Claassen M, Ori A, Szymborska A, Herzog F, Rinner O, Ellenberg J, and Aebersold R. in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:549 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 59 LC/MS/MS
runs from U2-OS cell lysates.
The data was published by
Beck M, Schmidt A, Malmstroem J, Claassen M, Ori A, Szymborska A, Herzog F, Rinner O, Ellenberg J, and Aebersold R. in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:549 (PubMed).
This study provides a large set of consistently good quality, journeyman data focussed on creating a catalog of proteins
present in a common cell line. The U2-OS line was derived from a female sarcoma with very few normal chromosomes and hypertriploid chromosome counts.
The cell culture used appears to have relatively clean, with little if any evidence of the presence of viruses or Mycoplasma. Any group
interested in quantifying unlabelled proteomics data, investigating rare post-translational modifications or developing
quality control metrics should take a look at this data.
 The common Repository of Adventitious Protein (cRAP)
list of proteins has been updated to
included three new proteins and a substitution for an obsolete sequence identifier. These changes
have been made to all of the GPM search servers and the new sequence files can be obtained at
ftp://ftp.thegpm.org/fasta/crap. Two
of the proteins (SRPP_HEVBR and REF_HEVBR) are characteristic of contamination with latex rubber, selected
based on an experimental determination of the proteins observed from macerated latex gloves
(see the data here).
The common Repository of Adventitious Protein (cRAP)
list of proteins has been updated to
included three new proteins and a substitution for an obsolete sequence identifier. These changes
have been made to all of the GPM search servers and the new sequence files can be obtained at
ftp://ftp.thegpm.org/fasta/crap. Two
of the proteins (SRPP_HEVBR and REF_HEVBR) are characteristic of contamination with latex rubber, selected
based on an experimental determination of the proteins observed from macerated latex gloves
(see the data here).
The
changes were as follows:
 This data set consisted of 37 LC/MS/MS
runs and summaries, from multidimensional chromatography experiments.
The data was published by
Barbhuiya MA, Sahasrabuddhe NA, Pinto SM, Muthusamy B, Singh TD, Nanjappa V, Keerthikumar S, Delanghe B, Harsha HC, Chaerkady R, Jalaj V, Gupta S, Shrivastav BR, Tiwari PK, and Pandey A. in
Proteomics. 2011 Dec;11(23):4443-53 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 37 LC/MS/MS
runs and summaries, from multidimensional chromatography experiments.
The data was published by
Barbhuiya MA, Sahasrabuddhe NA, Pinto SM, Muthusamy B, Singh TD, Nanjappa V, Keerthikumar S, Delanghe B, Harsha HC, Chaerkady R, Jalaj V, Gupta S, Shrivastav BR, Tiwari PK, and Pandey A. in
Proteomics. 2011 Dec;11(23):4443-53 (PubMed).
This series of multidimensional chromatography runs using high resolution MS and HCD MS/MS did exactly what
the title said: it provides a comprehensive catalogue of the proteins and consistituent peptides that
are to be expected when human bile is analyzed. It contains many best-to-date observations of proteins, even
ones that are not normally associated with bile, such as hornerin and dermcidin. The methods used produced
surprisingly good recovery of cysteine-containing peptides, which are often depleted in proteomics measurements.
Data set of the week: (2012/02/05)
Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 128 experiments
representing LC/MS/MS runs coupled with targeted affinity purification methods.
The data was published by
Bantscheff M, Hopf C, Savitski MM, Dittmann A, Grandi P, Michon AM, Schlegl J, Abraham Y, Becher I, Bergamini G, Boesche M, Delling M, Dümpelfeld B, Eberhard D, Huthmacher C, Mathieson T, Poeckel D, Reader V, Strunk K, Sweetman G, Kruse U, Neubauer G, Ramsden NG and Drewes G. in
Nat Biotechnol. 2011 29:255-65 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 128 experiments
representing LC/MS/MS runs coupled with targeted affinity purification methods.
The data was published by
Bantscheff M, Hopf C, Savitski MM, Dittmann A, Grandi P, Michon AM, Schlegl J, Abraham Y, Becher I, Bergamini G, Boesche M, Delling M, Dümpelfeld B, Eberhard D, Huthmacher C, Mathieson T, Poeckel D, Reader V, Strunk K, Sweetman G, Kruse U, Neubauer G, Ramsden NG and Drewes G. in
Nat Biotechnol. 2011 29:255-65 (PubMed).
The results demonstrate that the best way to find and quantitate relatively rare proteins is to utilize a targeted-affinity
purification approach. The protocols described in the paper work very well and the measurements were
well done. The peptide identification work in the paper was rather cursory, but that does not affect the biological conclusions or
the validity of the approach.
Data set of the week: (2012/01/29)
Modularity and hormone sensitivity of the Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor/target of rapamycin interaction proteome. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 138 experiments
representing LC/MS/MS runs from individual affinity purification protocols.
The data was published by
Glatter T, Schittenhelm RB, Rinner O, Roguska K, Wepf A, Jünger MA, Köhler K, Jevtov I, Choi H, Schmidt A, Nesvizhskii AI, Stocker H, Hafen E, Aebersold R, and Gstaiger M. in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:547. (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 138 experiments
representing LC/MS/MS runs from individual affinity purification protocols.
The data was published by
Glatter T, Schittenhelm RB, Rinner O, Roguska K, Wepf A, Jünger MA, Köhler K, Jevtov I, Choi H, Schmidt A, Nesvizhskii AI, Stocker H, Hafen E, Aebersold R, and Gstaiger M. in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:547. (PubMed).
This study was a good example of the routine use of good quality proteomics technology to elucidate an interesting
aspect of biology. It examined the protein-protein interactions associated with the InR/TOR pathway in the well-established
Kc167 cell line. The measurements were unambigious, resulting in a significant number of indentifications of relatively
rare D. melanogaster proteins involved in this pathway. It also contained a nice survey of the detectable SNAPs present in this
cell line — fruit flies have a surprisingly large number of nsSNPs compared to mammal genomes.
Data set of the week: (2012/01/22)
Characterization of the Asia Oceania Human Proteome Organisation Membrane Proteomics Initiative Standard using SDS-PAGE shotgun proteomics. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 6 experiments
from LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Peng L, Kapp EA, McLauchlan D, and Jordan TW. in
Proteomics 2011 11:4376-84 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 6 experiments
from LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Peng L, Kapp EA, McLauchlan D, and Jordan TW. in
Proteomics 2011 11:4376-84 (PubMed).
These experiments provide insight into how straightforward it has become to identify membrane proteins. Using a fairly
simple sample preparation method and LC/MS/MS with an LTQ instrument, the results show that it is possible to easily
identify large numbers of membrane proteins. It is still common for people to suggest that membrane proteins are
"difficult" using proteomics techniques. These results show that they are really no more difficult than
any other class of protein, so long as they can be kept in solution long enough to be digested.
 The Request-For-Comments GPM-2011.12.14
entitled "Nomenclature for the description of protein sequence modifications" has been
adopted by the GPM. The RFC describes a systematic method for recording modifications associated with protein sequences,
which can also be used to formulate queries about protein modifications to any compliant database system. GPM and
GPMDB will be modified over then next few months to be compliant with this new specification. We'd like
to thank everyone who sent in comments, almost all of which ended up in the final version of
the document.
The Request-For-Comments GPM-2011.12.14
entitled "Nomenclature for the description of protein sequence modifications" has been
adopted by the GPM. The RFC describes a systematic method for recording modifications associated with protein sequences,
which can also be used to formulate queries about protein modifications to any compliant database system. GPM and
GPMDB will be modified over then next few months to be compliant with this new specification. We'd like
to thank everyone who sent in comments, almost all of which ended up in the final version of
the document.
Data set of the week: (2012/01/15)
Deep proteome and transcriptome mapping of a human cancer cell line. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 164 experiments
from multidimensional LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Nagaraj N, Wisniewski JR, Geiger T, Cox J, Kircher M, Kelso J, Pääbo S, and Mann M. in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:548 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 164 experiments
from multidimensional LC/MS/MS runs.
The data was published by
Nagaraj N, Wisniewski JR, Geiger T, Cox J, Kircher M, Kelso J, Pääbo S, and Mann M. in
Mol Syst Biol. 2011 7:548 (PubMed).
This data set is an extensive investigation of how many peptides can be identified from the limited proteome of a
single human cell line using a combination of straight-forward LC/MS/MS
methods, multidimensional chromatography and multiple proteases, adding in high resolution MS/MS via HCD, and doing careful,
consistently state-of-the-art lab work. For the large number of groups that use HeLa cells, this work should serve
as a reference for what can be seen and what sort of experiment should be done to see it. For anyone interested in bioinformatics
and algorithm development, the scale (> 200,000 protein identifications) and precision of the work makes it an excellent
example for trying out new ideas. It is also an excellent raw data set to find novel post-translational modifications, splice
variants, viral contaminants and amino acid polymorphisms.
Data set of the week: (2012/01/08)
iPRG-2011: Study Materials for Identification of Electron Transfer Dissociation (ETD) Mass Spectra. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 1 SCX fraction
LCMS/MS run on a Thermo Orbitrap-LTQ hybrid instrument.
The data was made available on TRANCHE by the ABRF iPRG group
Robert J Chalkley, Nuno Bandeira, John Cottrell, Eric Deutsch, Eugene A. Kapp, Henry H. Lam, W. Hayes McDonald and Thomas Neubert
and has been described on the iPRG web site.
This data set consisted of 1 SCX fraction
LCMS/MS run on a Thermo Orbitrap-LTQ hybrid instrument.
The data was made available on TRANCHE by the ABRF iPRG group
Robert J Chalkley, Nuno Bandeira, John Cottrell, Eric Deutsch, Eugene A. Kapp, Henry H. Lam, W. Hayes McDonald and Thomas Neubert
and has been described on the iPRG web site.
This rather oddball dataset provides more insight into the "chilli-cook-off" mentality associated with
evaluating bioinformatics algorithms than it does into the current real-world problems in biomedical research.
Tests of this sort can be useful when their goals are to provide feedback
to algorithm & user interface designers and to inform users of the characteristics of algorithm performance.
It is questionable as to whether any of such aims were achieved by analyzing this data set.
The data was artificially removed from context (only one of 21 SCX fractions was made available). The
sample preparation methods used generated very high levels of non-enzymatic cleavage (22% of observable peptides),
unusually high levels of asparagine deamination (48% of N-containing peptides) and peptide N-terminal glutamine
cyclization (88% of peptides with an N-terminal Q). The mass measurements had large parent ion and fragment
ion systematic errors (+5 ppm and -0.25 Da respectively) and standard deviations (4 ppm and 0.3 Da). The proteins
in the sample were heavily skewed towards the cytosolic proteins and the added human sequence standard proteins (Sigma UPS). The
lack of the other 20 fractions made it impossible to draw any conclusions about the relative observability of
the added UPS proteins (and the ribosomal E. coli protein contaminants in the UPS preparation). It was
very unclear why such a complex, poorly controlled sample/measurement combination was used to test
algorithms and so little information about the true character of the sample was provided to the participating
groups. This hidden complexity resulted in more of an examination of the detective abilities of the groups than a
useful test of the algorithms.
 The latest edition (2012.01.01) of both the GPM Homo sapiens and
Mus musculus Proteome Guides have been been made available. The Guides
are the results of an automated curation of the >200 million human and >50 million mouse peptide identifications in
GPMDB. The Guides use ENSEMBL v. 62 protein sequences and their chromosome coordinates
are aligned to the human GRCh37 genome and mouse NCBIM37 genome builds, respectively. The Guides are available either as spreadsheets or in HTML format and
they may be downloaded either from the links above or the GPM Annotation Project ftp server.
The latest edition (2012.01.01) of both the GPM Homo sapiens and
Mus musculus Proteome Guides have been been made available. The Guides
are the results of an automated curation of the >200 million human and >50 million mouse peptide identifications in
GPMDB. The Guides use ENSEMBL v. 62 protein sequences and their chromosome coordinates
are aligned to the human GRCh37 genome and mouse NCBIM37 genome builds, respectively. The Guides are available either as spreadsheets or in HTML format and
they may be downloaded either from the links above or the GPM Annotation Project ftp server.
Data set of the week: (2012/01/01)
Proteomic Analysis of a Pleistocene Mammoth Femur Reveals More than One Hundred Ancient Bone Proteins. Overall rating: 
 This data set consisted of 4 data sets
constructed from several different types of experiment.
The data was published by
Cappellini E, Jensen LJ, Szklarczyk D, Ginolhac A, da Fonseca RA, Stafford TW, Holen SR, Collins MJ, Orlando L, Willerslev E, Gilbert MT, and Olsen JV. in
J Proteome Res. 2011 Dec 14 (PubMed).
This data set consisted of 4 data sets
constructed from several different types of experiment.
The data was published by
Cappellini E, Jensen LJ, Szklarczyk D, Ginolhac A, da Fonseca RA, Stafford TW, Holen SR, Collins MJ, Orlando L, Willerslev E, Gilbert MT, and Olsen JV. in
J Proteome Res. 2011 Dec 14 (PubMed).
This data was a truly amazing example of what can be obtained using samples that have
simply sat around outside for 43,000 years. The preservation of the detectable peptides was unexpectedly good.
The experiments were state-of-the-art at all levels and the data should be examined extensively by any
group interested in detecting amino acid polymorphisms associated with evolutionary change. The
analysis in the original paper was correct at the top level (the proteins detected) but was less well done at the level of
amino acid polymorphisms and side chain modifications. There are several more publications' worth of information
in this extraordinary data.
Copyright © 2012, The Global Proteome Machine Organization
|